Research
| Line 513: | Line 513: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="2" style="background:#8FBC8F; text-align:center; padding:1px; border-bottom:1px #8FBC9F solid;" | | | colspan="2" style="background:#8FBC8F; text-align:center; padding:1px; border-bottom:1px #8FBC9F solid;" | | ||
| − | <h2 style="margin:.1em; border-bottom:1px; font-size:140%; font-weight:bold;"> | + | <h2 style="margin:.1em; border-bottom:1px; font-size:140%; font-weight:bold;"> Complete Synthesis Methodology </h2> |
|- | |- | ||
| valign="top" style="padding:8px 8px 0px 8px; background:#f5fffa;" <!--H210 S4 V100--> | | | valign="top" style="padding:8px 8px 0px 8px; background:#f5fffa;" <!--H210 S4 V100--> | | ||
| − | + | Due to the stochastic nature | |
| + | of nano-fabrication, nano arrays show different properties both | ||
| + | in structural and physical device levels compared to conventional | ||
| + | technologies. Mentioned factors introduce random characteristics | ||
| + | that need to be carefully considered by synthesis process. For instance, a competent synthesis methodology must consider basic | ||
| + | technology preference for switching elements, defect or fault rates | ||
| + | of the given nano switching array and the variation values as well | ||
| + | as their effects on performance metrics including power, delay, and | ||
| + | area. Presented synthesis methodology in this study comprehensively covers the all specified factors and provides optimization | ||
| + | algorithms for each step of the process. | ||
| − | [[Image:Research- | + | [[Image:Research-synthesis-methodology.png|center|none|800px|link=]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<!-- YAYIN --> | <!-- YAYIN --> | ||
| Line 555: | Line 550: | ||
|- valign=top | |- valign=top | ||
| width="100" |'''title''': | | width="100" |'''title''': | ||
| − | | width="450"|[[Media: | + | | width="450"|[[Media: Morgul_EtAl_Integrated_Synthesis_Methodology for_Crossbar_Arrays.pdf | Integrated Synthesis Methodology for Crossbar Arrays]] |
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| '''authors''': | | '''authors''': | ||
| − | + | | width="450"| Ceylan Morgul, Luca Frontini, Onur Tunali, Ioana Vatajelu, Valentina Ciriani, Lorena Anghel, Csaba Moritz, Mircea Stan, Dan Alexandrescu, and Mustafa Altun | |
| − | + | |- valign="top" | |
| − | + | ||
| − | | width="450"| | + | |
| − | |- valign=top | + | |
| '''presented at''': | | '''presented at''': | ||
| − | | width="450"| [http:// | + | | width="450"|[http://www.nanoarch.org/ IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Nanoscale Architectures (NANOARCH)], Athens, Greece, 2018. |
|} | |} | ||
| align=center width="70" | | | align=center width="70" | | ||
<span class="plainlinks"> | <span class="plainlinks"> | ||
| − | [[File:PDF.png|65px|link=http://www.ecc.itu.edu.tr/images/ | + | [[File:PDF.png|65px|link=http://www.ecc.itu.edu.tr/images/b/b1/Morgul_EtAl_Integrated_Synthesis_Methodology_for_Crossbar_Arrays.pdf]]</span> |
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | [[Media: | + | [[Media: Morgul_EtAl_Integrated_Synthesis_Methodology_for_Crossbar_Arrays.pdf | Paper]] |
| align="center" width="70" | | | align="center" width="70" | | ||
<span class="plainlinks"> | <span class="plainlinks"> | ||
| − | [[File:PPT.jpg|60px|link=http://www.ecc.itu.edu.tr/images/ | + | [[File:PPT.jpg|60px|link=http://www.ecc.itu.edu.tr/images/b/bd/Morgul_EtAl_Integrated_Synthesis_Methodology_for_Crossbar_Arrays.pptx]] |
</span> | </span> | ||
| − | <br> [http://www.ecc.itu.edu.tr/images/ | + | <br> [http://www.ecc.itu.edu.tr/images/b/bd/Morgul_EtAl_Integrated_Synthesis_Methodology_for_Crossbar_Arrays.pptx Slides] |
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 15:57, 13 May 2019
We aim to develop a complete synthesis and performance optimization methodology for switching nano-crossbar arrays that leads to the design and construction of an emerging nanocomputer. Our objectives are 1) synthesizing Boolean functions with area optimization; 2) achieving fault tolerance; 3) performing performance optimization by considering area, delay, power, and accuracy; 4) implementing arithmetic and memory elements; and 5) realizing a synchronous state machine.
Contents |
Logic Synthesis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
We study implementation of Boolean functions with nano-crossbar arrays where each crosspoint behaves as a diode, a FET, and a four-terminal switch. For these three types, we give array size formulations for a given Boolean function. Additionally, we focus on four-terminal switch based implementations and propose an algorithm that implements Boolean functions with optimal array sizes. 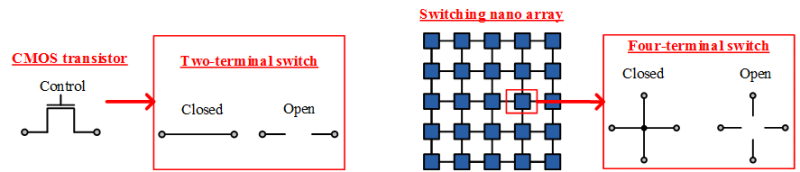
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fault Tolerance | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
We examine reconfigurable crossbar arrays by considering randomly occurred stuck-open and stuck-closed crosspoint faults. In the presence of permanent faults, a fast and accurate heuristic algorithm is proposed that uses the techniques of index sorting, backtracking, and row matching. In the presence of transient faults, tolerance analysis is performed by formally and recursively determining tolerable fault positions Since density feature of crossbar architectures is the main attracting point, we perform a detailed yield analysis by considering both uniform and non-uniform defect distributions. We formalize an approximate successful mapping probability metric for uniform distributions and determine area overheads. 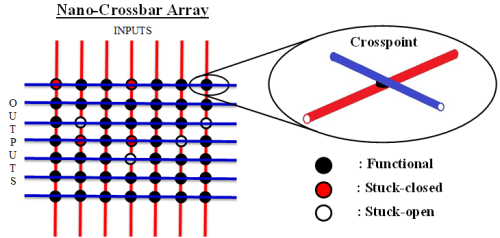
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Performance Modeling and Analysis | |||||||||||||
|
We introduce an accurate capacitor-resistor model for nano-crossbar arrays that is to be used for power/delay/area performance analysis and optimization. In order to find capacitor and resistor values, we investigate upper/lower value limits for technology dependent parameters including doping concentration, nanowire dimension, pitch size, and layer thickness. We also use different fan-out capacitors to test the integration capability of these technologies. 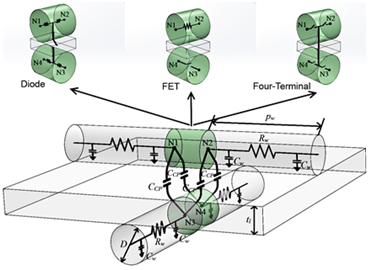
| |||||||||||||
Technology Development and Performance Optimization | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Nano-crossbar arrays have emerged as a strong candidate technology to replace CMOS in near future. They are regular and dense structures. Computing with crossbar arrays is achieved by its crosspoints behaving as switches, either two-terminal or four-terminal. Depending on the technology used, a two-terminal switch behaves as a diode, a resistive/memristive switch, or a field effect transistor (FET). On the other hand, a four-terminal switch has a unique behavior. While there have been many different technologies proposed for two-terminal switch based arrays, technology development for four-terminal switch based arrays, called switching lattices, has recently started. For both two-terminal and four-terminal switch based arrays, we aim to develop a complete synthesis and performance optimization methodology for switching nano-crossbar arrays that leads to the design and construction of an emerging nanocomputer. We also aim to develeop CMOS-compatible technologies for crossbar arrays, specifically for switching lattices. 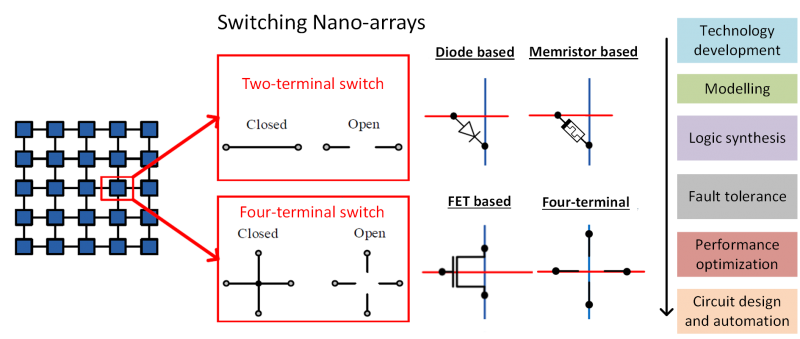 Technology DevelopmentAlthough a four-terminal switch based array offers a significant area advantage, in terms of the number of switches, compared to the ones having two-terminal switches, its realization at the technology level needs further justifications and raises a number of questions about its feasibility. We answer these questions. First, by using three dimensional technology computer-aided design (TCAD) simulations, we show that four-terminal switches can be directly implemented with the CMOS technology. For this purpose, we try different semiconductor gate materials in different formations of geometric shapes. Then, by fitting the TCAD simulation data to the standard CMOS current-voltage equations, we develop a Spice model of a four-terminal switch. Finally, we successfully perform Spice circuit simulations on four-terminal switches with different sizes. 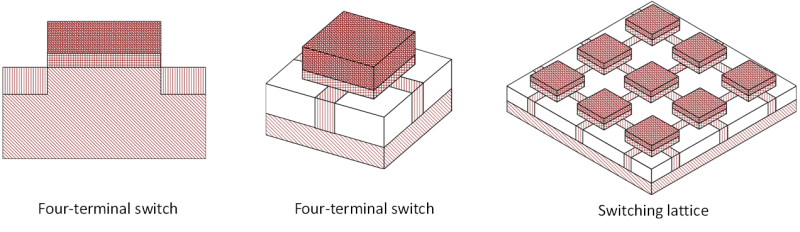 Performance OptimizationWe study crossbar arrays including the memristive ones. We propose a defect-tolerant logic synthesis algorithms by considering area, delay, and power costs of the arrays.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Complete Synthesis Methodology | ||||||||||||
|
Due to the stochastic nature of nano-fabrication, nano arrays show different properties both in structural and physical device levels compared to conventional technologies. Mentioned factors introduce random characteristics that need to be carefully considered by synthesis process. For instance, a competent synthesis methodology must consider basic technology preference for switching elements, defect or fault rates of the given nano switching array and the variation values as well as their effects on performance metrics including power, delay, and area. Presented synthesis methodology in this study comprehensively covers the all specified factors and provides optimization algorithms for each step of the process. 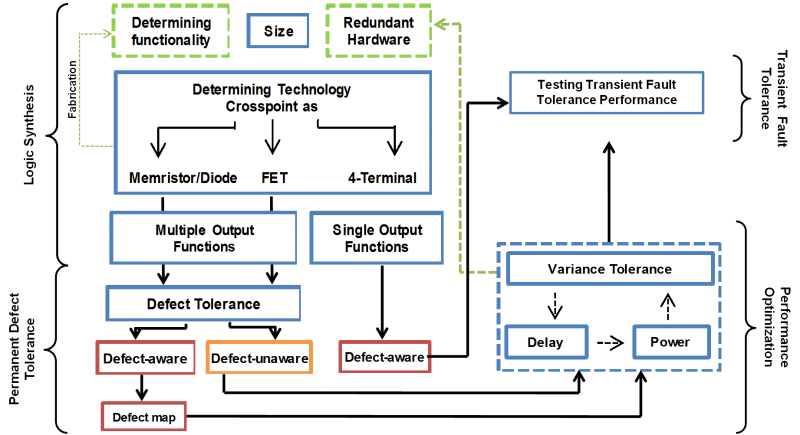
|
||||||||||||


